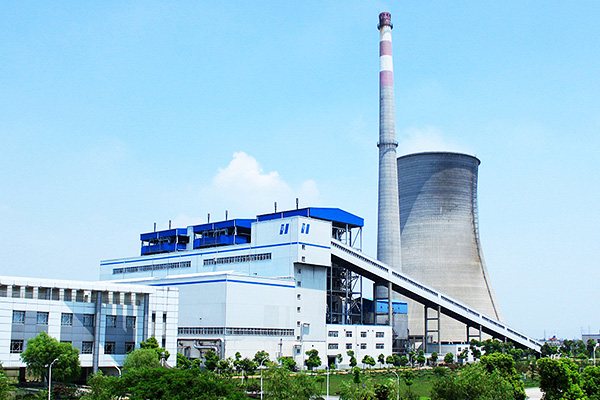
Boiler and Auxiliaries In Coal Fired Thermal Power Station
For centuries, coal based thermal power plants provide electricity for industrial and residential use, which plant converts the chemical energy of the coal into electrical energy. This is achieved by raising the steam in the boilers, expanding it through the turbine and coupling the turbines to the generators which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. A Steam Boiler essentially is a container into which water can be fed and steam can be taken out at desired pressure, temperature and flow.
The basic components of Boiler are:
Furnace and Burners
Steam and Superheating
a)Low temperature superheater
b) Platen superheater
c) Final superheater
Economiser
It is located below the LPSH in the boiler and above pre heater. It is there to improve the efficiency of boiler by extracting heat from flue gases to heat water and send it to boiler drum.
Air Preheater
The heat carried out with the flue gases coming out of economiser are further utilized for preheating the air before supplying to the combustion chamber. It is a necessary equipment for supply of hot air for drying the coal in pulverized fuel systems to facilitate grinding and satisfactory combustion of fuel in the furnace
Reheater
Power plant furnaces may have a reheater section containing tubes heated by hot flue gases outside the tubes. Exhaust steam from the high pressure turbine is rerouted to go inside the reheater tubes to pickup more energy to go drive intermediate or lower pressure turbines.
Steam turbines
Steam turbines have been used predominantly as prime mover in all thermal power stations. The steam turbines are mainly divided into two groups: –
Impulse turbine
Impulse-reaction turbine
The turbine generator consists of a series of steam turbines interconnected to each other and a generator on a common shaft. There is a high pressure turbine at one end, followed by an intermediate pressure turbine, two low pressure turbines, and the generator. The steam at high temperature (536 ‘c to 540 ‘c) and pressure (140 to 170 kg/cm2) is expanded in the turbine.
Condenser
 The condenser condenses the steam from the exhaust of the turbine into liquid to allow it to be pumped. If the condenser can be made cooler, the pressure of the exhaust steam is reduced and efficiency of the cycle increases.
The condenser condenses the steam from the exhaust of the turbine into liquid to allow it to be pumped. If the condenser can be made cooler, the pressure of the exhaust steam is reduced and efficiency of the cycle increases.
Boiler feed pump
Boiler feed pump is a multi stage pump provided for pumping feed water to economiser. BFP is the biggest auxiliary equipment after Boiler and Turbine. It consumes about 4 to 5 % of total electricity generation.
Cooling tower
The cooling tower is a semi-enclosed device for evaporative cooling of water by contact with air. The hot water coming out from the condenser is fed to the tower on the top and allowed to tickle in form of thin sheets or drops. The air flows from bottom of the tower or perpendicular to the direction of water flow and then exhausts to the atmosphere after effective cooling.
Fan or draught system
In a boiler it is essential to supply a controlled amount of air to the furnace for effective combustion of fuel and to evacuate hot gases formed in the furnace through the various heat transfer area of the boiler. This can be done by using a chimney or mechanical device such as fans which acts as pump.
Forced draught: – In this system a fan called Forced draught fan is installed at the inlet of the boiler. This fan forces the atmospheric air through the boiler furnace and pushes out the hot gases from the furnace through superheater, reheater, economiser and air heater to stacks.
Induced draught: – Here a fan called ID fan is provided at the outlet of boiler, that is, just before the chimney. This fan sucks hot gases from the furnace through the superheaters, economiser, reheater and discharges gas into the chimney. This results in the furnace pressure lower than atmosphere and affects the flow of air from outside to the furnace.
Balanced draught:-In this system both FD fan and ID fan are provided. The FD fan is utilized to draw control quantity of air from atmosphere and force the same into furnace. The ID fan sucks the product of combustion from furnace and discharges into chimney. The point where draught is zero is called balancing point.
Ash handling system
The disposal of ash from a large capacity power station is of same importance as ash is produced in large quantities. Ash handling is a major problem.
Generator
Generator or Alternator is the electrical end of a turbo-generator set. It is generally known as the piece of equipment that converts the mechanical energy of turbine into electricity. The generation of electricity is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.




