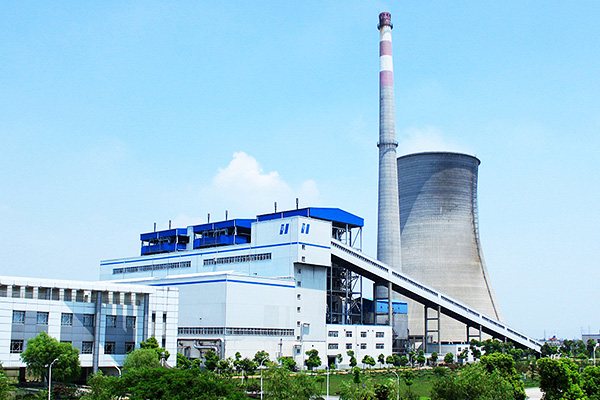
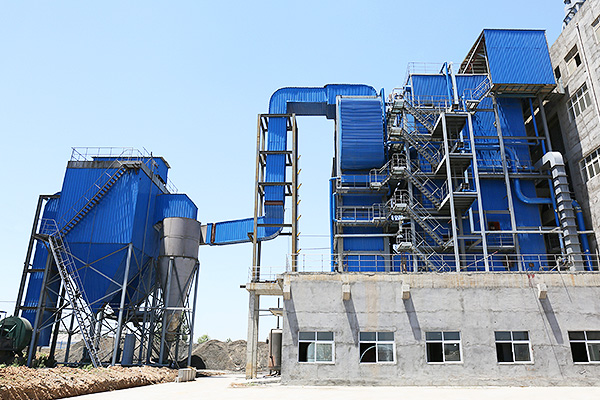
Co-generation Boiler Manufacturers for Sugar Plants
Cogeneration of bagasse is one of the most attractive and successful energy projects that have already been demonstrated in many sugarcane producing countries such as Mauritius, Reunion Island, India and Brazil. Combined heat and power from sugarcane in the form of power generation offers renewable energy options that promote sustainable development, take advantage of domestic resources, increase profitability and competitiveness in the industry, and cost-effectively address climate mitigation and other environmental goals.
What is co-generation?
Co-generation is the concept of producing two forms of energy from one fuel. One of the forms of energy must always be heat and the other may be electrical or mechanical energy. In a conventional power plant, fuel is burnt in a boiler to generate high-pressure steam which is used to drive a turbine, which in turn drives an alternator through a steam turbine to produce electrical power. The exhaust steam is generally condensed to water which goes back to the boiler. As the low-pressure steam has a large quantum of heat which is lost in the process of condensing, the efficiency of conventional power plants is only around 35%. In a cogeneration plant, very high efficiency levels, in the range of 75%–90%, can be reached. This is so, because the low-pressure exhaust steam coming out of the turbine is not condensed, but used for heating purposes in factories or houses.
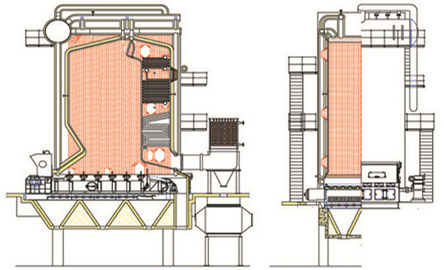
Co-generation of bagasse boiler in sugar plants
The sugar mills in India, Brazil, Mauritius and other countries consume their own bagasse to run their mills and generate steam to run the boilers and turbines; they generate power to run their plants. Sometimes, the surplus energy can be exported to the grid of distribution licensees.




